Instructions
We can skip the next cell if neural_de was installed from pip install.
[1]:
import sys
sys.path.append("..")
import time
Let’s import neural_de
[3]:
from neural_de.transformations.resolution_enhancer import ResolutionEnhancer
We load an example image
[4]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
start=time.time()
input_path = Path('../examples/images/fox.jpg')
image = cv2.imread(str(input_path))
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
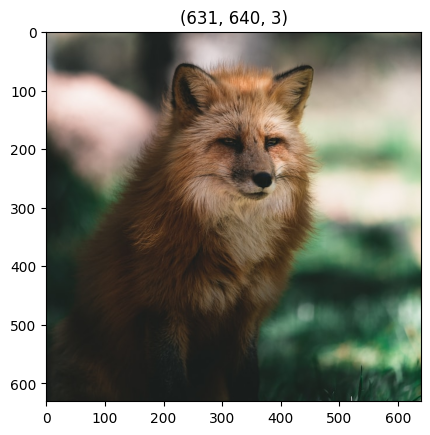
plt.imshow(image)
plt.title(image.shape)
[4]:
Text(0.5, 1.0, '(631, 640, 3)')
Enhancing an image
We create an instance of ResolutionShift :
If you want to upsample multiple images and have a GPU, it is adviced to install torch with cuda enabled and use device=’cuda’, as upsampling can take a lot of time without.
[7]:
shifter = ResolutionEnhancer(device='cpu')
[03-19 17:14:09] {C:\SAUVEGARDES_FIN_CONFIANCE\FONDATION\Support_composants\NeuralDE\examples\..\neural_de\utils\twe_logger.py:123} INFO - Logger: name: neural_de_logger, handlers: [<StreamHandler stdout (DEBUG)>]
[03-19 17:14:09] {C:\SAUVEGARDES_FIN_CONFIANCE\FONDATION\Support_composants\NeuralDE\examples\..\neural_de\transformations\resolution_enhancer.py:63} INFO - ResolutionEnhancer Initialized
We apply the transform method to any number of images.
we can have multiple images per call of transform, and call transform multiple time with the same shifter.
for now, only ratio=2 is available for upsampling, as the underlaying transformer was trained for a 2x resolution.
[8]:
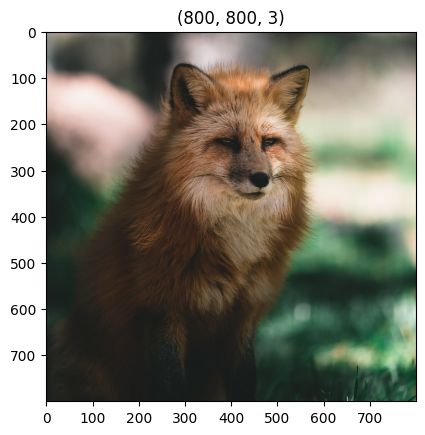
upsampled = shifter.transform([image], target_shape = (800, 800))
[03-19 17:14:11] {C:\SAUVEGARDES_FIN_CONFIANCE\FONDATION\Support_composants\NeuralDE\examples\..\neural_de\transformations\resolution_enhancer.py:72} INFO - Swin2 model loaded to cpu
[9]:
plt.imshow(upsampled[0])
plt.title(upsampled[0].shape)
[9]:
Text(0.5, 1.0, '(800, 800, 3)')
Improving image quality without changing the resolution
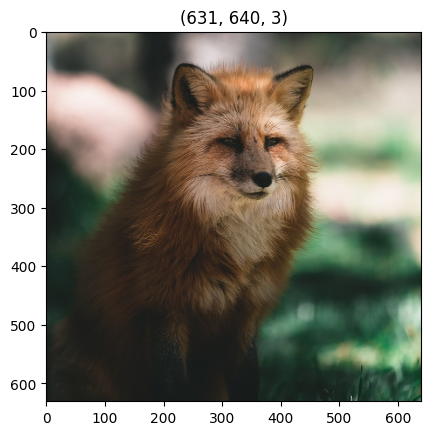
Using transform with output shape the same as the original image can still improve its quality.
[10]:
improved = shifter.transform([image], target_shape=image.shape[:2])
[11]:
plt.imshow(improved[0])
plt.title(improved[0].shape)
[11]:
Text(0.5, 1.0, '(631, 640, 3)')
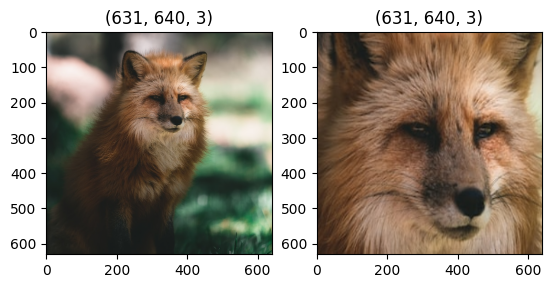
Working with batch
You can provide a batch of image to transform().
All the images will be resized to target_shape.
It supports images of different sizes as inputs.
[12]:
another_image = image[100:300, 200:450]
improved_images = shifter.transform([image, another_image], target_shape=image.shape[:2])
[13]:
for i in range(2):
plt.subplot(1,2,i+1)
plt.imshow(improved_images[i])
plt.title(improved_images[i].shape)
Include image with a crop ratio
ratio: foat value in range [0, 1[
[14]:
# crop input image by 70%
improved = shifter.transform([image], target_shape=image.shape[:2], crop_ratio=.7)
plt.imshow(improved[0])
plt.title(improved[0].shape);
[03-19 17:16:36] {C:\SAUVEGARDES_FIN_CONFIANCE\FONDATION\Support_composants\NeuralDE\examples\..\neural_de\utils\twe_logger.py:123} INFO - Logger: name: neural_de_logger, handlers: [<StreamHandler stdout (DEBUG)>]
[15]:
end=time.time()
print("temps final : ",end-start)
temps final : 209.8618779182434
[ ]:
[ ]:
[ ]: